Breast Augmentation
- Home
- -
- Plastic Surgery
- -
- Breast Surgery
- -
- BREAST AUGMENTATION

BREAST AUGMENTATION BRIEFLY
Procedure time
1 - 2 hours
Anesthesia
General
hospital stay
1 night
time off work
7-10 days
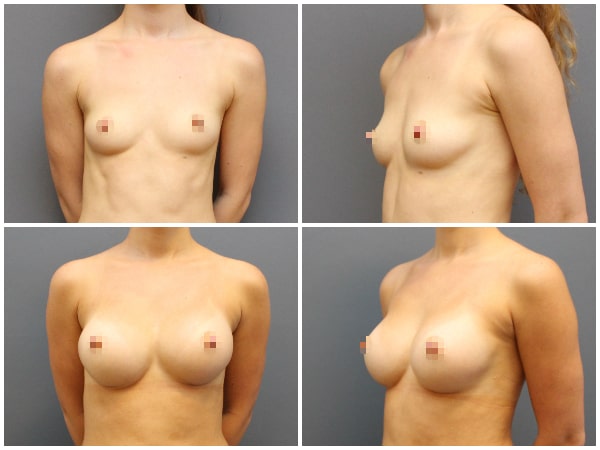
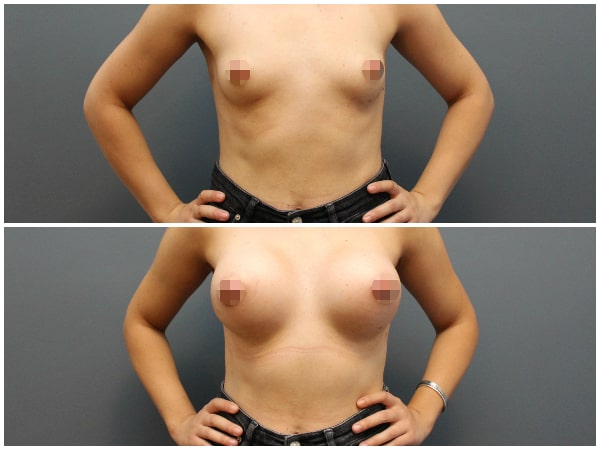
Augmentation mammoplasty is the surgical procedure by which we achieve breast enlargement using silicone implants. Breast augmentation is indicated for women with small breasts by nature or breasts that have lost volume after pregnancy or weight loss.
The implants are inserted through a small incision either in the crease under the breast or around the nipple and sometimes in the armpit. They are placed above or under the breast muscle called pectoralis major muscle. The operation takes about 2 hours under general anesthesia.
What should I expect after surgery?
The patient stays in the clinic overnight. One should expect mild pain that is addressed with standard painkillers. Mild swelling is present during the first week which subsides gradually. A special brassiere must be worn for 4-6 weeks after surgery.
Is there any problem with breastfeeding?
During breast augmentation we do not intervene with the milk ducts. There is therefore minimal risk that future breastfeeding is affected.
Is the result permanent? Will I need to change the implants?
Silicone implants are very durable and safe. However, you may need to change them in case of capsular contracture or implant rupture.
Before & after photos
BREAST AUGMENTATION BRIEFLY
Duration of surgery
1 - 2 hours
Anesthesia
General
Stay at the clinic
1 night
Return to work
7-10 days