OTOPLASTY
- Home
- -
- Plastic Surgery
- -
- Facial Surgery
- -
- OTOPLASTY

OTOPLASTY BRIEFLY
Procedure Time
1 - 2 hours
Anesthesia
Local (General in children)
Hospital stay
3 - 4 hours
Time off work
7-10 days
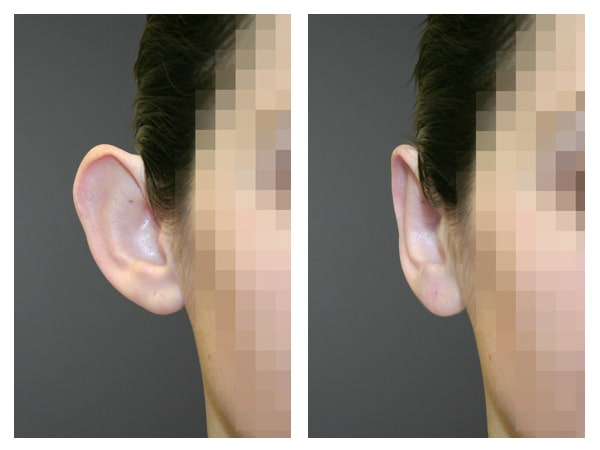
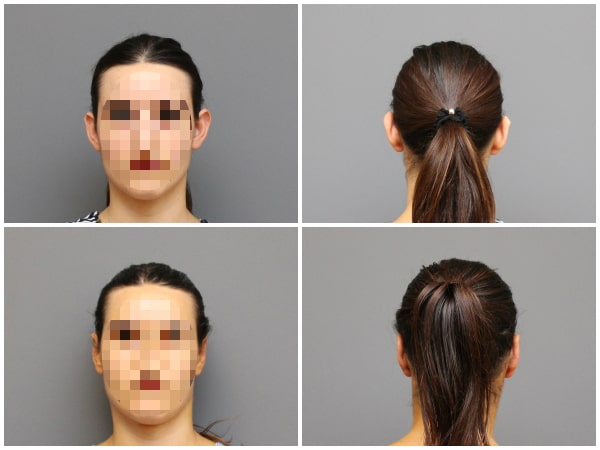
Protruding ears, a relatively common congenital condition, often result from either turbinate hypertrophy or the absence of antihelices, with occasional coexistence of both factors. This condition usually affects both ears but it can be detected at only one side.
Otoplasty, a corrective procedure, addresses this anomaly by reshaping the ear’s cartilage. The incision is discreetly put on the posterior surface of the ear, ensuring minimal visibility.
When is surgery for protruding ears recommended?
The ear reaches 85-90% of its adult size by the age of 5-6, making surgical correction possible at this stage. Early intervention is advisable to spare children from potential psychological distress. However, otoplasty remains a viable option at any age.
What type of anaesthesia is used?
Otoplasty is typically performed under local anaesthesia and generally takes around two hours. General anaesthesia is reserved for children in order to minimise patient distress.
What to expect after surgery?
Following the surgery, patients wear an elastic bandage around the ears for one week. Postoperative discomfort is mild and can be managed with standard pain relievers. Bruising and swelling are common after surgery and gradually subside within a few days. The patient needs to wear a protective elastic band(i.e tennis ribbon) around the ears during sleep for the next couple of months.
Before & after photos
OTOPLASTY BRIEFLY
Duration of surgery
1 - 2 hours
Anesthesia
Local (General for kids)
Stay at the clinic
Some hours
Return to work
7-10 days